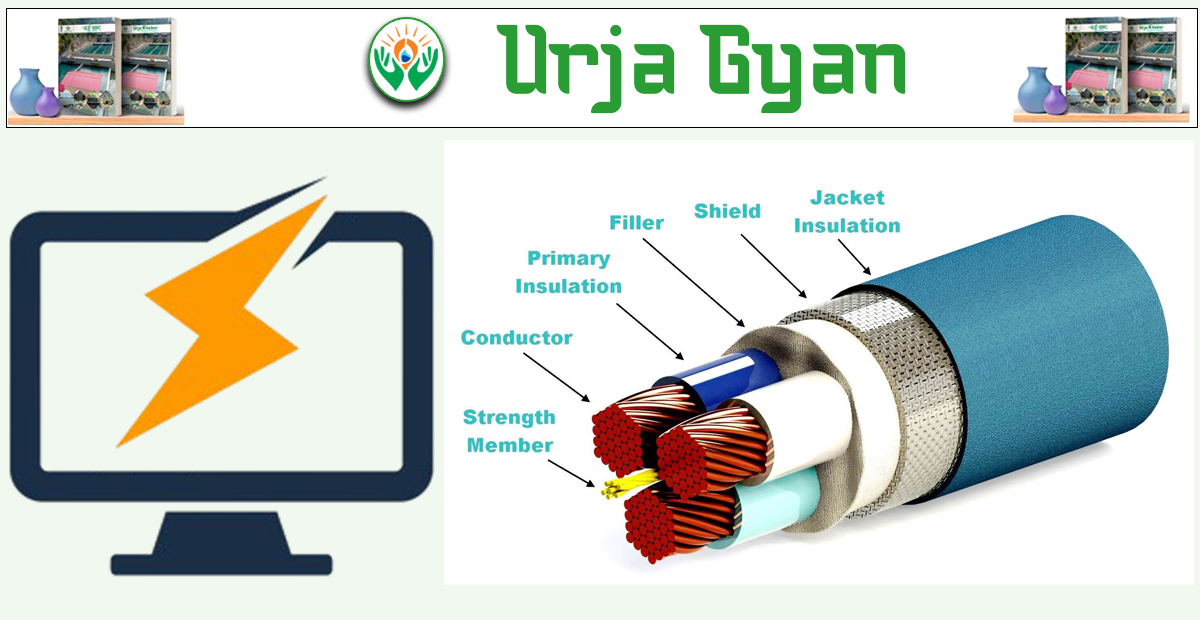
Kathmandu: Under the "Urja Gyan" column, an attempt is made to provide insight into the types of electrical cables (conductors) used for electricity flow. Last week, we discussed transmission lines, their types, and applications.
1. What is an Electrical Cable (Conductor)?

Answer: An insulated electric cable is a conductor that one can touch safely without electric shock. The material used for insulation is a very high resistance, non-conducting material that avoids current leakage. Depending on voltage and insulation material cables are of different types.
Insulated cables: These cables are inexpensive and therefore, normally used in low tension transmission lines carrying 400/ 230 volts.

XLPE insulated cables: These cables are normally used for voltages more significant than 11 kV.
2. Classification of Cables
Depending on Construction:
Unarmored Cable: Insulation is available only between conductor and outer.
Armored Cable: Under the outer, there are laminated layers of iron or aluminum. In this type, the cable can't be damaged by any means, physically, even with tools such as a hammer the conductor won't get affected.
ABC Cable (Aerial Bundled Cable): In ABC, 2, 3, or 4 wires are bundled together on the pole and carried by suspending through the air. So the name given Aerial Bundled Cable.
On the basis of Insulation
PVC Cables: Insulation of Polyvinyl Chloride, which is less expensive than XLPE.
XLPE Cables: Insulation of Cross-Linked Polyethylene, suitable to bear higher voltages.
According to the Conductor Material
Copper Cables: The conductor is made of copper, which is costlier than aluminum.
Aluminum Cables: Less expensive and lighter as compared to copper cables.
According to No. of Cores A core is a conductor containing many fine strands (strands). Cables are classified as Single-Core, Double-Core, Three-and-a-Half Core, Four-Core or Multi-Core. Three-and-a-Half Core cables have one conductor with half the cross-sectional area as compared to others used wherever the neutral current is very small. Multi-Core cables are used more often in control panels since more than 4 cores.
Dependent upon Voltage Rating
LT Cables (Low Tension) : It is applied to 400/230 volts supply.
HT Cables (High Tension) : It is used for supplies over 11 kV
Voltage Rating for house wiring cable:1100 volts.
Similarly, cables for 400-volt three-phase motors should be rated for 1100-volts.
Selection Based on Current Capacity: Every cable or conductor has a current-carrying capacity called ampacity. The capacity of the cable must be more than the load current.
Multiple-Choice Questions
XLPE stands for
(a) Cross-Linked Polyethylene
(b) Cross-Linked Polypropylene
(c) Xanthen-Linked Emulsion
(d) Xanadu-Linked Polyethylene
Answer: (a) Cross-Linked Polyethylene
XLPE is
(a) Good Conductor
(b) Poor Conductor
(c) Semiconductor
(d) None of the above
Answer: (b) Poor Conductor
The normal voltage-grade of LT power cables is
(a) 0.4 kV
(b) 1.0 kV
(c) 1.1 kV
(d) 3.3 kV
Answer: (c) 1.1 kV
ABC in cable terminology stands for
(a) Air Insulated Basic Cable
(b) Air Bipolar Cable
(c) Air Bundled Botanic Cable
(d) Air Bundled Cable
Answer: (d) Air Bundled Cable
The major component inside the converter is called
(a) Thyristor
(b) Inductor
(c) Fan
(d) Transistor
Answer: (a) Thyristor
At what temperature can the current-carrying capacity of a cable of PVC be maximum?
(a) 90°C
(b) 120°C
(c) 150°C
(d) 70°C
Answer: (d) 70°C
With regard to what the following is necessary in DC line?
(a) Phase Angle
(b) Voltage Sequence
(c) Voltage and Polarity
(d) Frequency
Answer: (c) Voltage and Polarity