Our country is blessed with the plentiful sunlight where people living in the diverse landscape has taken full advantage of the rising sun for the purpose of their use and the sunlight has played a crucial role in sustaining lives of millions of people in globe. As the demand for electricity continues to grow in Nepal and the need for sustainable energy resolution becomes more pressing, the solar power development has appeared as a most viable option for the country’s sustainable economic development and a pathway to focus on the revenue generation by the government.
As the preferences for the solar erection, installation has relied upon the traditional form of the contract, but there has been a significant shift towards EPC contracts and this new approach to the development reflects a holistic move to optimize the resources to manage risks so to ensure the timely completion of the development projects. In this document, I will try to link the advantages and disadvantages of the solar power plant installations procedures in Nepal, the current state of the solar project development and how the least developed country like Nepal can address the current context of land shortages while advancing its sustainable energy dreams based on the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.

In Nepal, the country faced the shortages of manpower that raises to think how we can bring back to our people so that they can work in Nepal for infrastructure and renewable energy that Nepal is developing and committed for 10,000 MW in ten years however, the major constraints Nepal facing is to find the non-usable land for the solar development. The major concerns today for the policy makers and the genuine developers is to manage the land for the construction and development of the solar energy farms which can be more stress for the government bodies in terms of food securities if not intended seriously. This article would also navigate how such development can leads to the pathway of sustainable energy deficit that currently Nepal is facing it in the remote location. The city headquarters and the outskirt are more reliable in the energy however, some part of the terrain is still facing the energy deficit. Recently, the demand for sustainable energy solutions has rushed, promoting developers and project stakeholders to actively engage in construction and installing solar energy projects across Nepal by investing more amount of money to buy the non-usable lands that the government shall cleared to drive for the development.
Recently, the government has taken a positive approach by inviting proposal for 960 MW with an additional 20% capacity to award the project for study and survey license so that the developers and relevant stakeholders can take into the feasibility studies to construct the projects. This initiative has attracted numerous national and international stakeholders to conduct and invest in the projects. In addition, it is the government line agencies like NEA, DOED and other electricity agencies who shall needs to be more flexible in adopting energy sustainable guidelines and policies to help sustain energy development in Nepal. The shift towards engineering, procurement and construction contracts has been driven by various factors which recognizes and provides a single point of roles and responsibility for the entire development of project reducing coordination issues that often arise with multiple contractors. The EPC contractors bring expertise and efficiency to the table, ensuring that all projects are completed to highest standards. In furtherance to that, with fixed pricing and timelines, EPC contracts can help minimize financial risks and delays, making them attractive to investors and the related project stakeholders to rely upon for the development and project execution.

As Nepal struggles with growing land deficit due to rapid urbanization and agricultural demands, innovative strategies are necessary to balance energy development with land use. One effective approach is to promote rooftop solar installations, which can harness energy from existing structures while significantly reducing land use. Furthermore, integrating solar panels with agricultural practices can optimize land utilization, allowing for dual purposes of food production and energy generation. Additionally, the developers in collaboration with the government and other private organizations, can also utilize brownfield sites that has been either used or contaminated lands for solar development projects. This idea shall minimize the impact on agricultural areas and protects valuable farmland.
Encouraging community based solar projects can further distribute energy generation while fostering local participation and investment. As previously mentioned, there are both advantages and disadvantages to solar installation in Nepal. One of the primary benefits is that solar energy is a renewable and abundant resource, contributing to energy independence and fostering economic growth. The relatively low construction and development costs associated with solar energy can make it an attractive option for developers and project charters. In furtherance to that, the solar sector has the potential to create numerous jobs in installation, maintenance, and manufacturing, encouraging local participation in the industry.
In the best opinion, solar energy also plays a crucial role in reducing carbon emissions, aligning with global climate goals to decrease greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, solar power plants can enhance grid stability, as distributed solar generation improves reliability and resilience for surrounding communities. On the downside, the initial investment costs can pose a barrier for many potential developers and related stakeholders, especially given the high costs associated with land acquisition or leasing for power plant development. The significant upfront expenses can be particularly challenging in the face of land demands driven by the rapid urbanization. Another disadvantage is the intermittency of solar energy production, which relies on weather conditions and the time of day. This necessitates energy storage solutions to ensure a consistent power supply for the communities. Competing land demands for agriculture for food production and urban development can also complicate the construction of solar projects in some context. In light of these challenges, the government of Nepal the energy section must consider policy-level outcomes that should come to the favour to the government bodies and the private developers to make solar installation and construction more robust and aligned with clean energy innovative solutions that shall meet the UN SDGs concept to make the city resilience in terms of energy efficient programs.
Encouraging community based solar projects can further distribute energy generation while fostering local participation and investment. As previously mentioned, there are both advantages and disadvantages to solar installation in Nepal. One of the primary benefits is that solar energy is a renewable and abundant resource, contributing to energy independence and fostering economic growth.
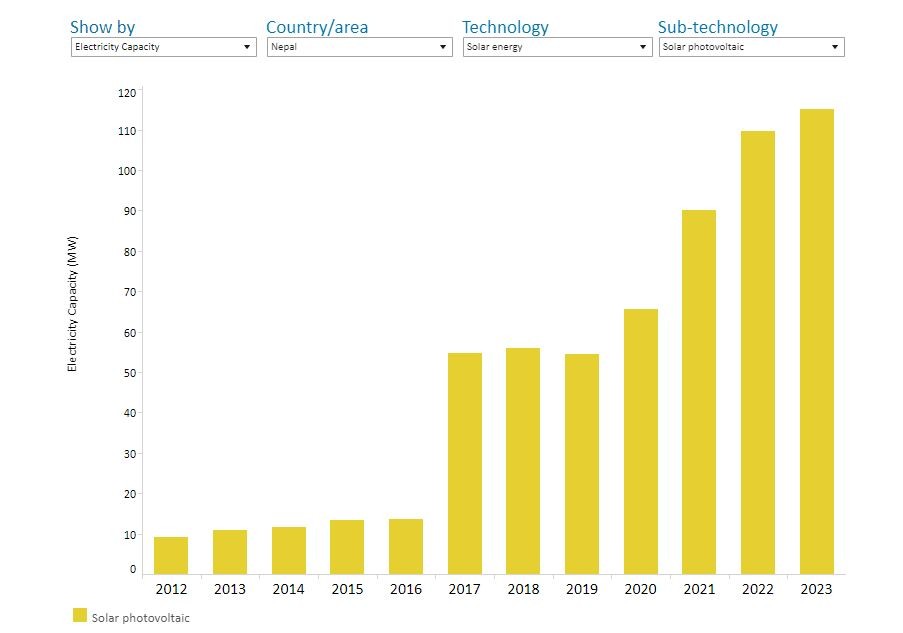
As from the different records available in the google and various research papers and company websites, Nepal has made notable progress in solar energy progress in solar energy construction, installation and development. The Government of Nepal through the Ministry of Energy, Water Resources, and Irrigation, along with the Department of Electricity, has issued licenses for the construction of solar farms across various regions in Nepal, with an estimated total capacity of 110.47 MW. Additionally, around 50 MW of solar projects are current under construction, highlighting the growing interest in solar energy production. The Nepal Electricity Authority (NEA) has approved several projects through its Request for Proposal (RFP) process, indicating a solid framework for solar project development. As it stands from the record that, Nepal's installed solar capacity is around 55 MW, producing over 133 GWh of energy annually. In context to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the solar energy is gaining traction worldwide, increasingly embraced by societies and communities for generating clean energy harnessed directly from the sun using solar photovoltaic and concentrated solar power technologies. The energy profile presented by IRENA for Nepal reveals significant disparities in capacity utilization between hydropower and solar energy in Nepal, with hydropower accounting for 56% and solar energy only by 12% in 2022. This information highlights the potential for growth in solar energy as the country seeks to diversify its energy sources. For a more detailed analysis and review, one must visit the site for the detailed information of the country profile documented by IRENA that provides comprehensive insights into the current state of the renewable energy in Nepal.
Similarly, Nepal faces challenges in solar energy development, the opportunities for growth and innovation are more substantial. By leveraging natural resources, embracing modern technologies like single facial, dual facial panels, transformers, inverters, and mostly focus on implementing supportive policies, Nepal can enhance its solar capacity and contribute significantly to reach its sustainable energy goals. The transition to solar power not only promises to meet the increasing energy demand but also helps in aligning with global efforts to combat climate change and promote economic development. As the country like Nepal navigates its energy landscape, a collaborative approach involving government, project charters, developers, stakeholders and the local communities will be essential to realize a sustainable, a cleaner, green future for all that strives to the present needs and the generation to come.
There are even both advantages and disadvantages, the best part of the solar energy is that it is the powerful resources that one can get a free sunlight that is abundant and sustainable, contributing to the energy independence that would foster economic growth, revenue generation to the government and help sustain energy businesses that has low cost in terms of construction and development. The following information are excerpt from the energy profile of Nepal of year 2022.

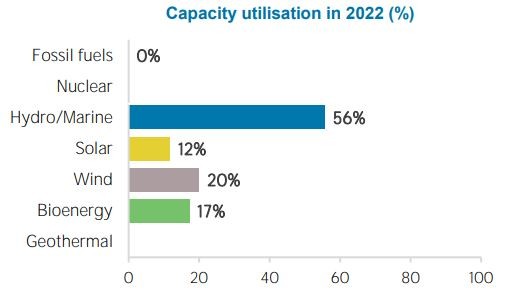 Source: IRENA Country Energy Profile, 2022
Source: IRENA Country Energy Profile, 2022
In context of an achieving and embracing solar energy, it is a significant step towards achieving several united nation sustainable development goals. One of the most critical goals is Goal 7, which aims to ensure access to affordable and clean energy for all. By expanding the provision of access to solar energy, the country can provide universal access to electricity, which is a fundamental right for its citizens and can be sold out to collect the revenue for the economic growth of the country. In addition, the growth of solar energy in Nepal also contributes to reach Goal 13, the climate action, as it reduces the county’s reliance on fossil fuels and supports climate resilience and mitigation strategies. In furtherance to that, the solar sector has the potential to foster job creation and economic diversification in Nepal aligning with Goal 8 decent work and economic growth. As the country continues to invest in solar energy, it can create new employment opportunities and stimulate local economies.
To accelerate the transition to renewable energy sources, including solar and hydropower, the government can implement and manage policies such as carbon taxation. This can incentivize the adoption of clean energy sources and support Nepal’s commitment to climate action. In addition, the government can offer tax incentives for solar installations, which can drive sustainable growth while addressing environmental challenges. To link this, our national planning commission should also prioritize fiscal policies that can support the adoption of the electric vehicles which can further enhance Nepal’s commitment to climate action and climate resilience. By promoting EVs, Nepal can reduce its carbon footprint and can create a cleaner, healthier environments for all his citizens living in the communities. However, the journey towards a sustainable energy future through solar contracting is marked by innovative solutions so as the land constraint issues would be affecting the developers and the stakeholders, the government shall encourage the public land to be used for the constructive approach to utilize the best efforts with ideas to squeeze the issues of the land challenges that can impact in future.
As the country continues to expand in its development, it must deliberately develop a mechanism to focus on the vertical expansion of the solar development that shall be developed in the cities, in the complex building with mirror facing technology that can embrace modern technological advancements, and implement supportive policies to secure a sustainable for the current needs and the future generations to come. I believe that Nepal's growth in solar energy is a crucial step towards achieving sustainable development goals and mitigating climate change. By implementing supportive policies, promoting clean energy sources, and embracing innovative solutions, Nepal can create a sustainable energy future that benefits its citizens and the environment. The author of this article is a professional civil engineer by profession.
