Energy Update
Important Facts to Learn About Electricity Transmission and Distribution Lines
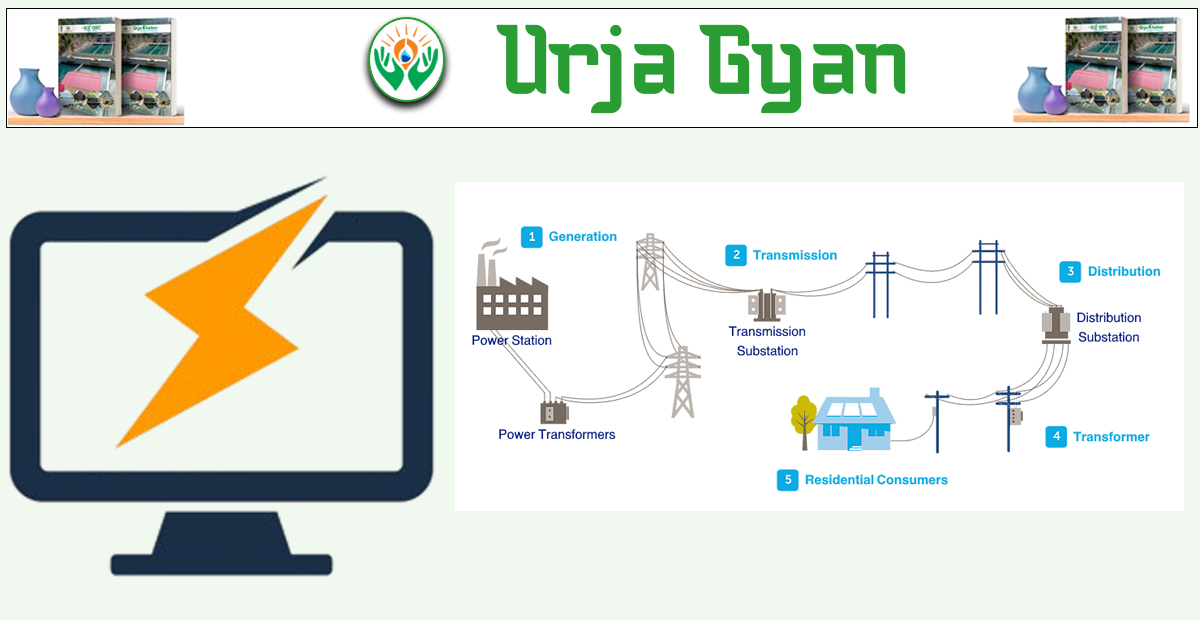
Kathmandu : In this week's learning segment "Urja Gyan", Urja Khabar presents to you important facts related to electricity transmission and distribution lines this week. Last week, we learned different issues such as electricity access, energy crisis, and possible solutions.
(1) What is electricity transmission?

Answer: Electricity transmission is the process of transporting electrical energy from where it is produced (for instance, power houses or water energy plants) to where it is consumed (for instance, homes, industries, companies).
(2) What are the main technical characteristics of electricity transmission?

Answer: The main technical characteristics of electricity transmission are:
- Purpose: To transfer electricity efficiently over long distances with minimum loss.
- Voltage level: High voltage levels (e.g., 132 kV, 220 kV, 400 kV) are used to reduce energy loss.
- Transmission lines: Mainly made up of overhead steel pylon towers or underground cables.
- Substations: Used to transform voltage levels.
- Transformers: Used for stepping up or stepping down voltage levels.
- AC or DC: Most of the transmission is carried out using Alternating Current (AC), but over very long distances, High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) is used, which can be more efficient in some cases.
(3) What is a grid system?
Answer: A grid system refers to the connection of transmission lines from power plants and consumption areas. It enhances sharing and reliability of electricity. For example, electricity from Upper Tamakoshi or Kali Gandaki A hydropower plants is transmitted to Kathmandu or somewhere with high-voltage transmission lines.
Grid system provides a continuous supply of power, consolidates electricity from various sources (hydro, solar, wind, thermal, biomass, etc.) into one, and maintains supply-demand balance in different regions.
(4) What is electricity distribution?
Answer: Electricity distribution is the passing of electricity from the transmission system to the consumers such as household buildings, businesses, industries, and agricultural farms.
(5) Principal components of electricity distribution:
Step-down transformers: Convert high-voltage electricity (transmission) to lower voltages (e.g., 33 kV, 11 kV, 400 V, or 230 V) in distribution substations.
Distribution lines:
- 33 kV and 11 kV lines: Supply power to cities, suburbs, and neighborhoods.
- 400 V / 230 V lines: Supply power directly to houses and small shops.
- Service connections: Final connection from the pole to the consumer's master switchboard or meter.
(6) Voltage levels for different consumers
- Residential places: 230 volts (single phase)
- Commercial places: 400 volts (three phase)
- Large industries: 11 kV or higher
(7) Course of electricity in a distribution system:
- Power station → Transmission line → Substation → Distribution line → Transformer → Consumer
For instance, electricity from the 132/33 kV Bharatpur substation is stepped down to 33 kV and distributed to domestic and industrial consumers through various feeders. Nepal Electricity Authority (NEA) is the primary electricity distributor in the majority of Nepal.
(8) General problems in the distribution system:
- Technical losses owing to lack of infrastructure
- Overloading of lines or transformers
- Theft of electricity from unauthorized connections
- Intermittent supply in rural or remote locations
(9) Function of a good distribution network:
- Ensures continuous supply to every consumer
- Economical growth facilitation
- Supports reduction in system losses and maximum efficiency guarantee
Conversation
- Info. Dept. Reg. No. : 254/073/74
- Telephone : +977-1-5321303
- Email : [email protected]














