Energy Update
Electricity Access, Energy Crisis, and Solutions

Kathmandu : In this week's special series of the weekly education column "Urja Gyan" published every Friday by Urja Khabar, today we plan to provide some informations on the topic "Electricity Access, Energy Crisis, and Solutions." Last week, we published a technical and informative article entitled "Step Potential, Touch Potential, and Ground Resistance Reduction."
(1) What is electricity access?

Answer: Electricity access means having affordable and reliable electricity that one can utilize to meet every day's requirements. For example, if electricity is available to be utilized for lighting purposes, for cooking, for running appliances like TVs, refrigerators, and fans, for charging mobile phones and other appliances, or for running tools for work or business purposes, then electricity access is said to exist.
(2) Why is electricity access necessary everywhere in the world?

Answer: Currently, almost 700 million people worldwide remain without access to electricity. They are found primarily in Africa and South Asia's rural areas. Without electricity, they rely on candles, kerosene, or firewood—dirty and harmful sources of energy. Electricity is critical to education, medicine, poverty elimination, and overall development.
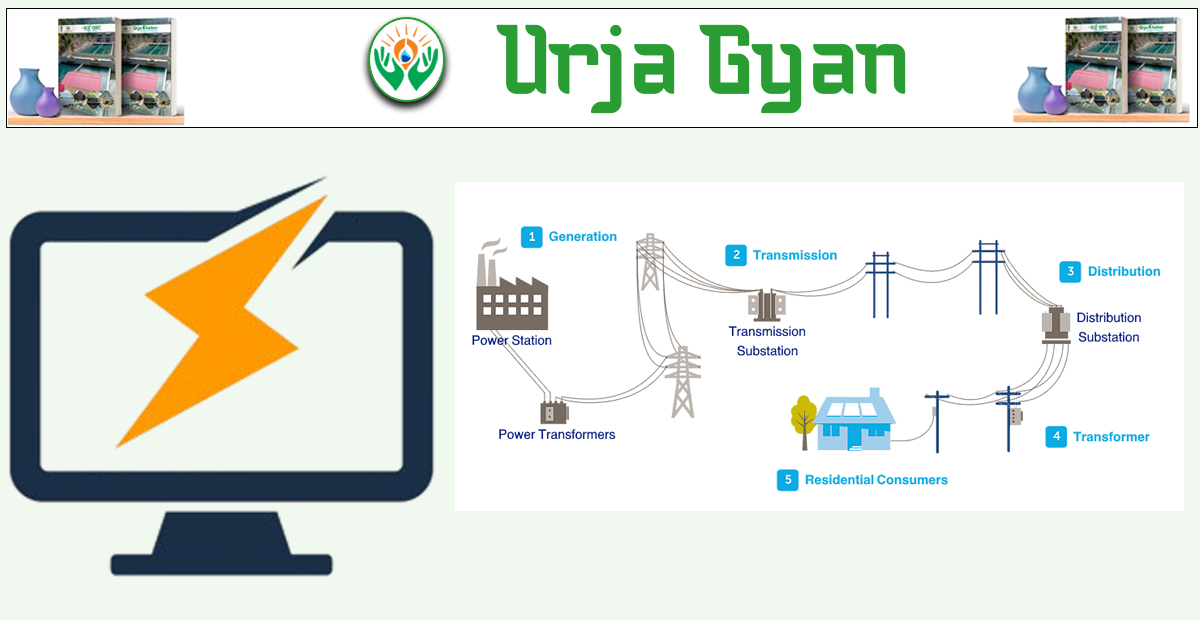
(3) What is the situation regarding electricity access in Nepal?
Answer: Currently, over 99% of Nepalese households are electrified. This has been achieved due to the establishment of the national grid, small hydropower schemes, solar photovoltaic systems, and other decentralized power systems. Yet there are some remaining challenges:
- Intermittent power outages in certain places
- Instability of power supply in far-flung villages
- Tariffs being too high or equipment costs rendering full utilization impossible
(4) Why is electricity access fundamental for development?
Answer: Electricity facilitates lighting, education, employment, healthcare, and improved living standards. It facilitates economic activities like agriculture, industries, and tourism. Use of clean energy encourages decreased environmental pollution and helps combat climate change.
(5) Define energy crisis.
Answer: An energy crisis means the lack of access to modern energy services—like electricity for lighting or clean fuel for cooking or heat. For example:
- No electricity in homes or businesses
- Use of impure fuels like firewood, dung, or kerosene
- Cant access secure, safe, and quality energy
- Unreliable or low-quality power supply
(6) What is the global status of the energy crisis?
Answer: Even today, over 700 million people lack access to electricity. The majority of them still use firewood or coal—dirty power. The energy crisis has negative effects on education, health, employment, and women's empowerment. It is often the case in Africa's rural areas, South Asia, and in conflict areas. Eliminating the energy crisis is part of the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goal 7.
(7) What is the situation for the energy crisis in Nepal?
Answer: Nepal has extended access to electricity to over 99% of the population, yet some remote villages lack a stable and secure supply. Power cuts or low voltage are common in the majority of places. Electric appliances or clean cooking fuel is unaffordable for the majority. Predominantly in rural places, over 65% of households still use firewood or biomass for cooking. Even after grid connection, the energy crisis continues.
The following circumstances point towards an energy crisis:
- Electricity is too expensive so frequent consumption is not feasible
- Supply is unstable or of poor quality
- Clean cooking facilities are unavailable or too costly
(8) Why is the energy crisis a critical issue?
Answer:
- The energy crisis is a critical issue because
- Indoor smoke significantly affects the health of children and women
- Inadequate illumination limits educational prospects
- Without electricity, industries or businesses cannot operate, reducing economic productivity
- It causes perpetuation of poverty and inequality
(9) What are the solutions to the energy crisis?
Answer: To address the energy crisis, the following can be done:
- Increase supply of clean, affordable, and reliable electricity
- Promote solar systems and mini-grids in off-grid areas
- Popularize clean cooking technologies (like electric stoves, biogas, etc.)
- Promote energy-efficient appliances and make them economically viable
Conversation
- Info. Dept. Reg. No. : 254/073/74
- Telephone : +977-1-5321303
- Email : [email protected]