Energy Update
How electricity is transmitted from the power station to villages and homes ?
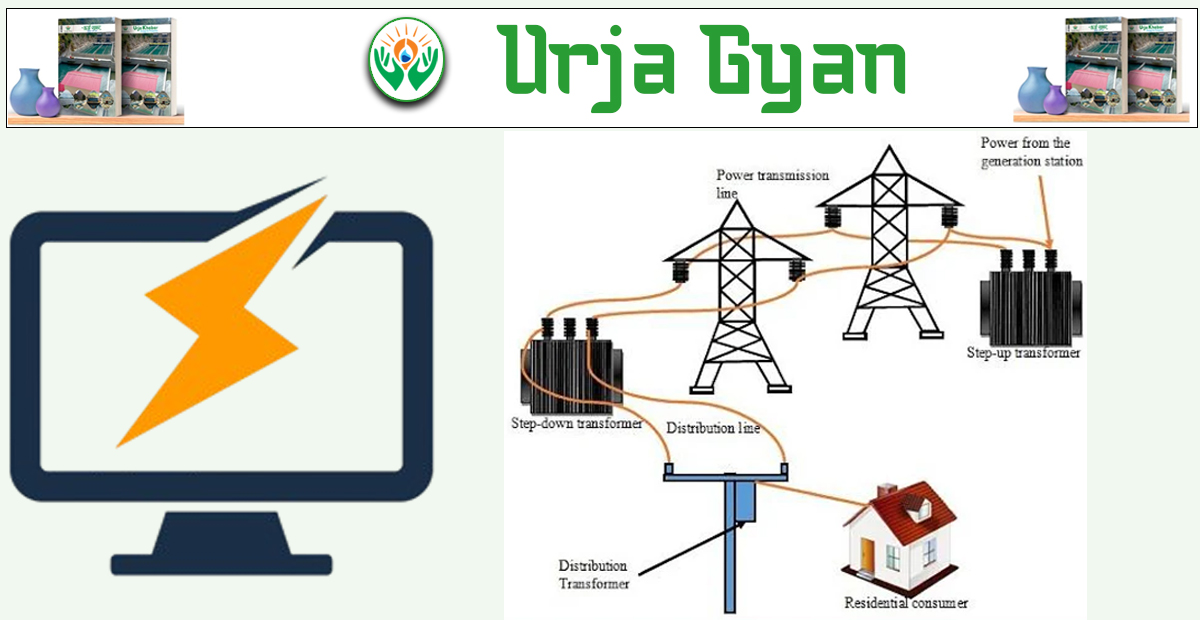
Kathmandu : Under the informative column "Urja Gyan" published every Friday by Urja Khabar, this week we have made an effort to provide information on electricity transmission and distribution, as well as related topics. Last week, we discussed various aspects of electrical current.
How is electricity transmitted from one place to another ?

Answer: After electricity is generated at a power plant, it is transmitted to villages and cities through wires suspended on poles or towers. These towers are made of many iron pieces. The electric wires must not touch these iron poles or towers, so insulators are used to prevent contact. In other words, insulators are placed between the poles or towers and the wires to prevent them from touching.
When electricity needs to be transmitted over long distances from the powerhouse, towers are used. For example, electricity from the Trishuli and Kulekhani powerhouses is transmitted to Kathmandu using towers. From the power plant, electricity is carried via towers to the substations. The voltage of electricity transmitted via these towers is usually 66,000V, 132,000V, 220,000V, 400,000V, or even higher. In Nepal, so far, only 400,000V lines have been constructed.

For example, electricity coming from the Trishuli and Sun Koshi powerhouses to Kathmandu is 66,000V, while electricity from the Marsyangdi powerhouse is 132,000V.
How electricity is distributed to homes?
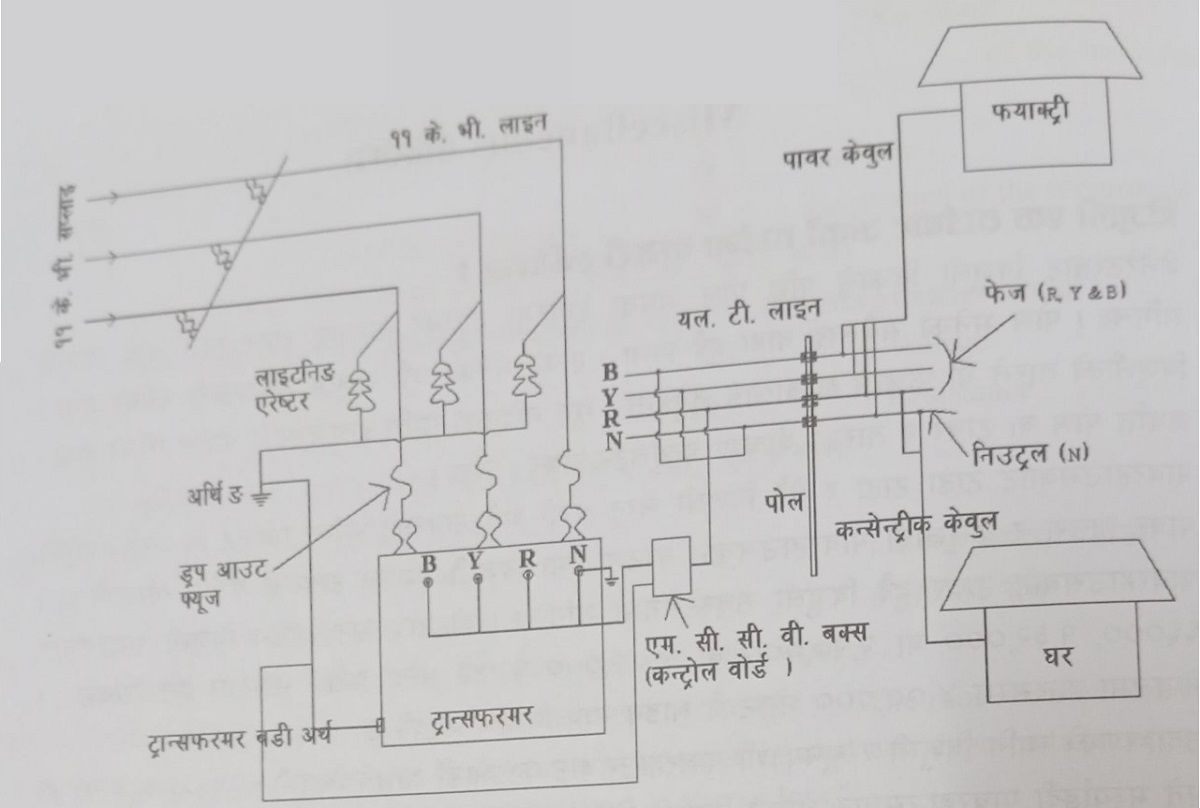
Answer: The electricity arriving at the substation is sent to a transformer at the substation. This transformer reduces the high voltage of 66,000V or 132,000V to 11,000V. This means that the incoming voltage of 66,000V or 132,000V is stepped down to 11,000V. The 11,000V electricity is then transmitted via wires mounted on iron, cement, or wooden poles to the cities and villages. This 11,000V line is often referred to as an 11KV (kilovolt) line.
From the substation, the 11kV line is extended to smaller transformers located in towns and villages. These smaller transformers, similar to the larger ones at the substation, have two sides: one side receives 11kV electricity, and the other side outputs 400V or 230V, depending on the requirements. For households, 230V electricity is supplied, while industries and factories may receive 400V.
The process of how electricity reaches homes and factories is illustrated in the diagram below.
 What is a fuse wire ?
What is a fuse wire ?
Answer: Although fuse wires are largely replaced by MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) and MCCB (Molded Case Circuit Breaker), they are still occasionally used. A fuse wire protects against electrical damage by breaking the circuit when excessive current flows. When there is a fault in a line, a large amount of current flows, which causes the fuse wire (a thin piece of metal) to melt, breaking the circuit and stopping further damage. In older homes, the main switch may have two Kit-Cats, which contain fuse wires. If the wires inside a home come into direct contact with each other, causing a fault, the fuse wire melts, and the circuit is broken, preventing further damage like fire.
Multiple Choice Questions:
How is current calculated ?
(a) By dividing voltage by resistance
(b) By dividing resistance by voltage
(c) By dividing power by voltage
(d) By dividing watt-hour by voltage
Answer: (a) By dividing voltage by resistance
What is the frequency of electricity distribution in Nepal ?
(a) 50 Hz
(b) 60 Hz
(c) 100 Hz
(d) 150 Hz
Answer: (a) 50 Hz
What happens when load A and load B are connected in parallel to the supply voltage?
(a) They receive different voltages
(b) They both receive the same voltage
(c) Only their currents are equal, voltage is not
(d) High voltage is generated
Answer: (b) They both receive the same voltage
What is the device that does not heat the glass or cup, but heats the contents inside?
(a) Thermos
(b) Microwave oven
(c) Electric heater
(d) Hot plate
Answer: (b) Microwave oven
Which device or method is used to check continuity?
(a) Multimeter
(b) Megger
(c) Supply voltage and bulb
(d) All of the above
Answer: (d) All of the above
In powerhouses and substations, what is DC supply used for?
(a) Emergency lighting
(b) Protection and control
(c) Transformers
(d) (a) and (b) both
Answer: (d) (a) and (b) both
What does the capacity of a battery generally refer to?
(a) Ampere-hour
(b) Volt-hour
(c) Watt
(d) Ampere
Answer: (a) Ampere-hour
Conversation
- Info. Dept. Reg. No. : 254/073/74
- Telephone : +977-1-5321303
- Email : [email protected]














