Kathmandu; As a part of the weekly column 'Urja Gyan' (Energy Knowledge) presented to you every Friday by Urja Khabar, this week we have data on diesel power plants and their advantages and disadvantages. We had written on renewable energy and its sources in our previous edition.
(1) What is a Diesel Power Plant?
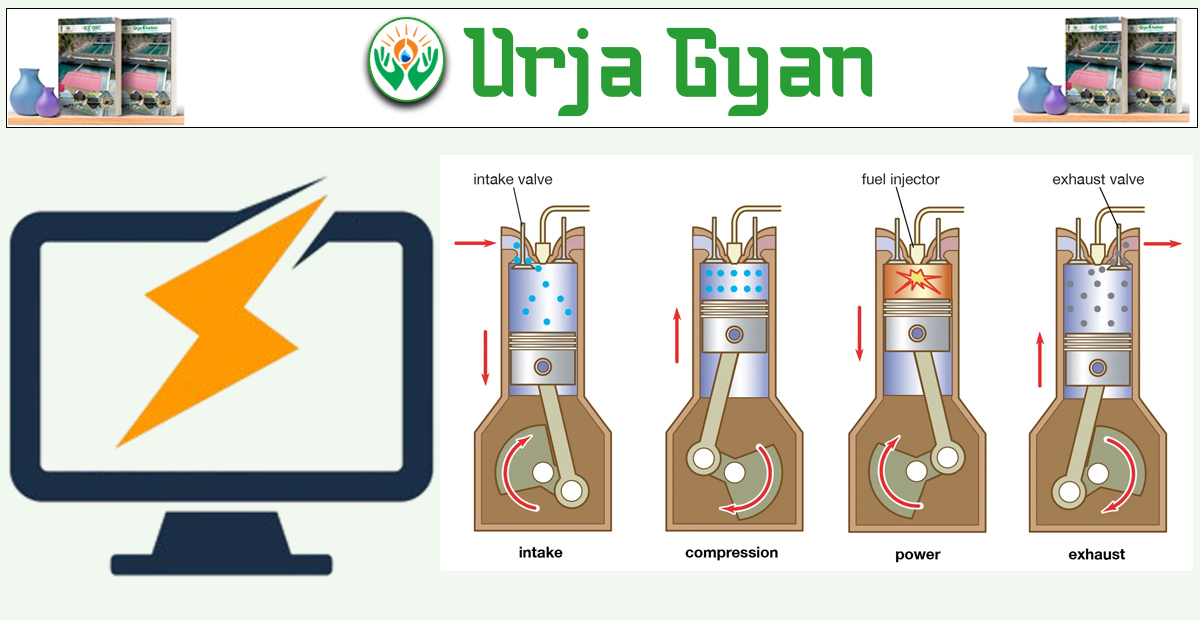
Answer: A diesel power plant is a thermal power generation unit where the power is produced by a diesel-driven engine. The plants are basically used as standby power supplies or in remote locations from the national power system.
(2) Principal Parts of a Diesel Power Plant:
 Diesel Engine: The principal part that creates mechanical energy by burning fuel.Alternator (Generator): Converts the engine's mechanical energy into electricity.
Diesel Engine: The principal part that creates mechanical energy by burning fuel.Alternator (Generator): Converts the engine's mechanical energy into electricity.
 Fuel System: Delivers and stores diesel to the engine.Air Intake and Exhaust System: Supplies clean air for combustion and exhausts the exhaust gases.Cooling System: Draws off excess heat from the engine (usually by water or air cooling).Lubrication System: Lowers friction to ensure smooth engine running.Control Panel: Controls and monitors parameters such as voltage, frequency, and temperature.Starting System: Usually battery-driven and activates an electric motor to start the engine.
Fuel System: Delivers and stores diesel to the engine.Air Intake and Exhaust System: Supplies clean air for combustion and exhausts the exhaust gases.Cooling System: Draws off excess heat from the engine (usually by water or air cooling).Lubrication System: Lowers friction to ensure smooth engine running.Control Panel: Controls and monitors parameters such as voltage, frequency, and temperature.Starting System: Usually battery-driven and activates an electric motor to start the engine.
(3) Diesel Power Plant Advantages:
Quick Start and Shutdown: Suitable for emergency and backup purposes due to its quick action.In Simple Design and Easy Installation: Small and simpler to install compared to thermal or hydro plants.Low Water Requirement: Less water needed for cooling purposes, hence suitable for water-deficient areas.High Efficiency at Partial Load: Efficient even during partial load situations.Low Cost of Capital: Lower to build compared to major hydro or thermal plants.Portability: Can be designed to be portable, hence convenient for offshore or short-term power projects.Reliability: Provides a steady output of electricity in the case of power failure or breakdown of the system.
(4) Drawbacks of Diesel Power Plants:
High Operating Expense: Diesel fuel is expensive, hence the high cost per unit of electricity produced.Limited Output: Not appropriate for the production of large quantities of electricity; typically used on small or medium loads.Air Pollution: Emits pollutants like carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, causing environmental issues.Noise Pollution: Emitted with great noise, requiring proper soundproofing.Requires Regular Maintenance: Requires skilled individuals for routine maintenance to keep the engine and its parts in top working condition.Dependent on Non-renewable Fuel: Relying on fossil fuel like diesel, which is market-dependent and non-renewable.